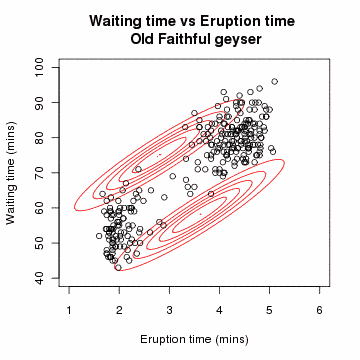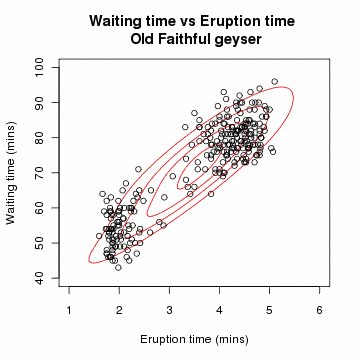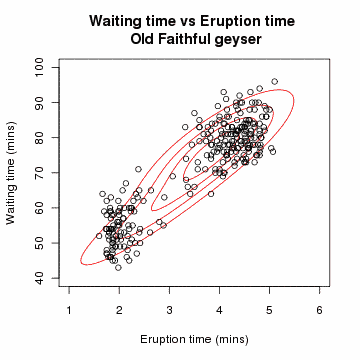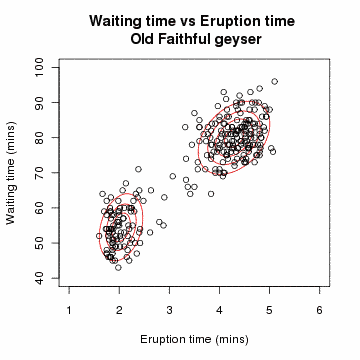
Clustering
Justin Donaldson
April-27-2017
Applied Machine Learning 410
(AKA: Birds of a feather)
Clustering History
Clustering first originated in anthropology
- Divide people into culturally similar groups
- “…matrilinear descent and avoidance of relatives-in-law were or tended to be inherently connected.”
Clustering Needs
“Data Clustering: 50 Years Beyond K-Means”, A.K. Jain (2008)
Overview
- Connectivity Clustering
- Centroid-based Clustering
- Density-based Clustering
- Graph-based Clustering
Connectivity-based clustering
Hierarchical Clustering
- Group together observations based on proximity in space.
- Agglomerative clustering (clusters grow from individual observations)
Hierarchical Clustering
For this analysis, let's look at arrest rates at a state level.
head(USArrests)
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape
Alabama 13.2 236 58 21.2
Alaska 10.0 263 48 44.5
Arizona 8.1 294 80 31.0
Arkansas 8.8 190 50 19.5
California 9.0 276 91 40.6
Colorado 7.9 204 78 38.7
Hierarchical Clustering
The arrest information is not expressed in distances, so we need to transform it.
as.matrix(dist(USArrests))[1:6, 1:6]
Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California Colorado
Alabama 0.00000 37.17701 63.00833 46.92814 55.52477 41.93256
Alaska 37.17701 0.00000 46.59249 77.19741 45.10222 66.47594
Arizona 63.00833 46.59249 0.00000 108.85192 23.19418 90.35115
Arkansas 46.92814 77.19741 108.85192 0.00000 97.58202 36.73486
California 55.52477 45.10222 23.19418 97.58202 0.00000 73.19713
Colorado 41.93256 66.47594 90.35115 36.73486 73.19713 0.00000
Hierarchical Clustering
R provides a good hierarchical clustering method in the standard distribution.
hc <-hclust(dist(USArrests))
hc
Call:
hclust(d = dist(USArrests))
Cluster method : complete
Distance : euclidean
Number of objects: 50
Hierarchical Clustering
Plotting it gives us a representation of the clusters in a tree-like form.
plot(hc, hang=-1)
Hierarchical Clustering
We can set a split point using “cutree”, which will give us the desired number of clusters
clusters = cutree(hc, k=5) # cut into 5 clusters
clusters
Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California
1 1 1 2 1
Colorado Connecticut Delaware Florida Georgia
2 3 1 4 2
Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa
5 3 1 3 5
Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland
3 3 1 5 1
Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri
2 1 5 1 2
Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey
3 3 1 5 2
New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Ohio
1 1 4 5 3
Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Rhode Island South Carolina
2 2 3 2 1
South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah Vermont
5 2 2 3 5
Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming
2 2 5 5 2
Hierarchical Clustering
We can overlay the cluster boundaries on the original plot.
plot(hc)
rect.hclust(hc, k=5, border="purple")
Hierarchical Clustering
USArrests[clusters==1,]
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape
Alabama 13.2 236 58 21.2
Alaska 10.0 263 48 44.5
Arizona 8.1 294 80 31.0
California 9.0 276 91 40.6
Delaware 5.9 238 72 15.8
Illinois 10.4 249 83 24.0
Louisiana 15.4 249 66 22.2
Maryland 11.3 300 67 27.8
Michigan 12.1 255 74 35.1
Mississippi 16.1 259 44 17.1
Nevada 12.2 252 81 46.0
New Mexico 11.4 285 70 32.1
New York 11.1 254 86 26.1
South Carolina 14.4 279 48 22.5
USArrests[clusters==2,]
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape
Arkansas 8.8 190 50 19.5
Colorado 7.9 204 78 38.7
Georgia 17.4 211 60 25.8
Massachusetts 4.4 149 85 16.3
Missouri 9.0 178 70 28.2
New Jersey 7.4 159 89 18.8
Oklahoma 6.6 151 68 20.0
Oregon 4.9 159 67 29.3
Rhode Island 3.4 174 87 8.3
Tennessee 13.2 188 59 26.9
Texas 12.7 201 80 25.5
Virginia 8.5 156 63 20.7
Washington 4.0 145 73 26.2
Wyoming 6.8 161 60 15.6
Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical Clustering
head(as.matrix(UScitiesD))
Atlanta Chicago Denver Houston LosAngeles Miami NewYork
Atlanta 0 587 1212 701 1936 604 748
Chicago 587 0 920 940 1745 1188 713
Denver 1212 920 0 879 831 1726 1631
Houston 701 940 879 0 1374 968 1420
LosAngeles 1936 1745 831 1374 0 2339 2451
Miami 604 1188 1726 968 2339 0 1092
SanFrancisco Seattle Washington.DC
Atlanta 2139 2182 543
Chicago 1858 1737 597
Denver 949 1021 1494
Houston 1645 1891 1220
LosAngeles 347 959 2300
Miami 2594 2734 923
Hierarchical Clustering
hc = hclust(dist(UScitiesD))
plot(hc)
rect.hclust(hc, k=3, border="purple")
Hierarchical Clustering
Options - Distance (good defaults)
- Euclidean \( \|a-b \|_2 = \sqrt{\sum_i (a_i-b_i)^2} \)
- Squared Euclidean \( \|a-b \|_2^2 = \sum_i (a_i-b_i)^2 \)
- Manhattan \( \|a-b \|_1 = \sum_i |a_i-b_i| \)
- Maximum Distance \( \|a-b \|_\infty = \max_i |a_i-b_i| \)
- Mahalanobis Distance : (\( S \) is the covariance matrix)* \( \sqrt{(a-b)^{\top}S^{-1}(a-b)} \)
Hierarchical Clustering
Options - Linkage (good defaults)
- single = closest neighbor to any point in cluster gets merged
- complete = closest neighbor to furthest point in cluster gets added
- UPGMA - Average of distances \( d(x,y) \) : \( {1 \over {|\mathcal{A}|\cdot|\mathcal{B}|}}\sum_{x \in \mathcal{A}}\sum_{ y \in \mathcal{B}} d(x,y) \)
- centroid - distance between average of points in cluster.
Centroid-based clustering
K-Means
K-means is the classic centroid-based technique.
kc <-kmeans(dist(USArrests), 5)
kc
K-means clustering with 5 clusters of sizes 14, 16, 6, 4, 10
Cluster means:
Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut
1 65.89233 96.07457 122.22107 34.09331 107.29421 39.87674 66.23308
2 44.26408 40.63415 39.30706 87.27907 39.61009 72.77326 164.91692
3 186.45199 215.61266 245.68765 140.62960 230.31143 157.96032 64.55080
4 156.66944 185.93502 216.79333 110.42542 202.23294 130.08173 41.33227
5 124.59232 154.48260 183.00204 79.98813 167.54319 95.46898 16.35455
Delaware Florida Georgia Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana
1 67.20616 163.01249 43.25800 128.64955 58.87385 78.34914 62.25396
2 43.22760 67.63373 65.42442 227.97517 155.25746 37.06141 160.84644
3 188.60864 286.62604 162.34794 29.11799 71.09903 201.14674 65.60171
4 159.44839 257.56938 132.83121 48.78623 41.13989 172.61816 38.83723
5 126.21743 224.00494 100.40272 69.53320 17.29587 138.34270 11.73799
Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland
1 119.61759 60.38700 69.05374 77.57022 94.96215 127.67658
2 218.49451 159.05258 165.84901 35.41213 192.58639 40.92104
3 14.16755 67.20859 61.09549 199.77363 36.21497 250.60974
4 27.51177 40.18894 31.37856 170.34344 10.30800 221.15908
5 58.35484 11.41076 16.54525 137.45393 35.62235 188.28510
Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana
1 33.42978 84.01840 102.76672 91.49070 25.05121 68.73604
2 126.79319 33.19452 202.03634 41.65756 96.36998 165.83229
3 103.59042 207.13296 27.68056 209.69053 130.14358 60.71176
4 77.80478 178.26311 18.60749 179.43873 101.66855 30.98355
5 42.53689 144.48241 41.89394 148.94802 67.55885 15.42239
Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York
1 73.57305 84.13843 118.95531 30.84698 113.01928 83.75387
2 172.20940 39.50211 217.71406 117.34247 34.10491 36.33470
3 54.11084 206.42920 14.53706 114.40486 236.19105 206.64587
4 27.42662 178.22988 26.55704 88.67804 206.94271 178.27364
5 14.93085 143.87782 57.75727 53.05615 173.70919 143.81224
North Carolina North Dakota Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania
1 166.51660 132.95563 55.24557 28.39951 26.41940 69.14625
2 72.99105 230.82548 153.98042 123.29857 115.23761 168.19979
3 287.09146 18.80491 74.13809 102.55246 111.32739 59.63153
4 256.98193 38.14490 49.16741 74.12040 83.03110 35.61800
5 225.92323 72.29857 15.74348 40.23432 49.30161 13.90017
Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah
1 31.90793 109.20147 92.90532 29.54413 35.75584 56.01761
2 104.36878 38.53295 189.73210 87.15383 74.93990 154.39390
3 127.97252 229.47582 40.03467 139.41307 153.83960 75.56577
4 101.13072 199.39953 10.66362 109.93988 125.76522 52.02789
5 66.64099 168.18393 34.94932 77.62259 91.00713 18.88683
Vermont Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming
1 132.66326 26.94074 32.76092 99.77677 121.86942 27.38481
2 229.09553 118.39457 129.17208 195.71986 221.20228 114.20837
3 25.21201 107.17384 98.05935 37.95290 16.55016 111.57683
4 38.98711 78.07427 70.91318 12.67582 32.83759 81.97383
5 73.55590 45.22863 36.11041 42.77453 60.72838 50.17080
Clustering vector:
Alabama Alaska Arizona Arkansas California
2 2 2 1 2
Colorado Connecticut Delaware Florida Georgia
1 5 2 2 1
Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa
3 5 2 5 3
Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland
5 5 2 4 2
Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri
1 2 4 2 1
Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey
5 5 2 3 1
New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Ohio
2 2 2 3 5
Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Rhode Island South Carolina
1 1 5 1 2
South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah Vermont
4 1 1 5 3
Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming
1 1 4 3 1
Within cluster sum of squares by cluster:
[1] 274120.554 608986.971 16906.656 5505.797 22532.254
(between_SS / total_SS = 90.4 %)
Available components:
[1] "cluster" "centers" "totss" "withinss"
[5] "tot.withinss" "betweenss" "size" "iter"
[9] "ifault"
K-Means
K-means is the classic centroid-based technique.
- Assignment Step : \( S_i^{(t)} = \big \{ x_p : \big \| x_p - m^{(t)}_i \big \|^2 \le \big \| x_p - m^{(t)}_j \big \|^2 \ \forall j, 1 \le j \le k \big\} \)
- Assign each data point to cluster whose mean is the smallest within-cluster sum of squares.
- Update Step : \( m^{(t+1)}_i = \frac{1}{|S^{(t)}_i|} \sum_{x_j \in S^{(t)}_i} x_j \)
- Calculate new centroids
K-Means
colors =brewer.pal(5, "Spectral")
arrests$clusters = colors[kc$cluster]
ggpairs(arrests, mapping=ggplot2::aes(fill=clusters,color=clusters))
K-Means
K-means is more sensitive to scaling
arrests = data.frame(scale(USArrests))
Quick aside on scaling
Field measurements can have different scales
dat = cbind(
x=rnorm(100, mean = 0, sd = 1),
y=rnorm(100, mean = -4, sd = 2),
z=rnorm(100, mean = 4, sd = 9)
)
boxplot(dat)
Quick aside on scaling
In some cases it may be useful to normalize the scales. Standard normalization:
- mean = 0
standard deviation = 1
boxplot(scale(dat))
K-means compared to Hierarchical Clustering
Hierarchical Clustering
- cluster count can be determined post hoc
- linkages are robust against scaling differences in fields
- good at extracting “strand” clusters
- quadratic time complexity : ~ \( O(n^2) \)
- repeatable
K-Means
- “k” cluster count must be given up front.
- scaling affects centroid calculation, consider normalizing if possible.
- good at extracting “spherical” clusters
- near-linear time complexity : ~ \( O(n) \)
- requires random initialization, results may not be repeatable in some cases
Distribution-based clustering
Bio break? - 15m
- Expectation Maximaztion
Expectation Maximization
- based on probability distributions
- no hard assignment of points to clusters, instead use probabilities
- underlying distributions can be anything, gaussians are common
Expectation Maximization
- Calculate expected value of log likelihood function:
\[
Q(\boldsymbol\theta|\boldsymbol\theta^{(t)}) = \operatorname{E}_{\mathbf{Z}|\mathbf{X},\boldsymbol\theta^{(t)}}\left[ \log L (\boldsymbol\theta;\mathbf{X},\mathbf{Z}) \right]
\]
- with respect to the conditional distribution of \( Z \) given \( X \) under the current estimate of the parameters \( \theta^{(t)} \).
- Find the parameter that maximizes : \[ \boldsymbol\theta^{(t+1)} = \underset{\boldsymbol\theta}{\operatorname{arg\,max}} \ Q(\boldsymbol\theta|\boldsymbol\theta^{(t)}) \]
Expectation Maximization
Plain english:
- Initialize \( \theta \) to one or more random values.
- Compute the best value for \( Z \) given the \( \theta \) values.
- Then use the computed values to compute a better value for \( \theta \).
- Rinse and repeat.
Expectation Maximization
EM works well when you have a good idea of the underlying distribution of the data. In this case, normal deviates
means = c(0,20,-15)
x = rnorm(300, means[1], 10)
y = rnorm(100, means[2], 1)
z = rnorm(100, means[3], 1)
dat = data.frame(x=c(x,y,z))
ggplot(data = dat,aes(x=x)) + geom_histogram()
Expectation Maximization
EM works well when you have a good idea of the underlying distribution of the data.
In this case, normal deviates
Expectation Maximization
library(EMCluster)
sem = shortemcluster(dat, simple.init(dat, nclass = 3))
em = emcluster(dat, sem, assign.class=T)
colors = brewer.pal(3, "Spectral")[em$class]
dat$class = colors
ggplot(data = dat, aes(x=x, fill=class)) + geom_histogram(position="dodge")
Expectation Maximization
EM models the distribution parameters, and can capture them even if distributions overlap.
em$Mu
[,1]
[1,] 20.0276881
[2,] 0.4845825
[3,] -15.0464675
as.matrix(means)
[,1]
[1,] 0
[2,] 20
[3,] -15
Expectation Maximization
Considerations
- If distribution characteristics are known, EM works well at recovering from noise and overlap in cluster boundaries.
- Parameterization includes cluster count and mixture model specification.
- Most similar to K-means, except cluster assignment is soft, rather than hard as in km.
Expectation Maximization
Strengths:
- Can easily adapt to different models/kernels (besides gaussian).
- Retrieves clusters and cluster model coefficients!
- Fast, iterative algorithm. Complexity depends on number of iterations and time to compute E and M steps.
Weaknesses:
- Requires more parameterization up front than any other model(cluster count, model expectation (e.g. gaussian), convergence, tolerance, etc.)
- Complexity dependent on chosen model parameters.
Density-based Clustering
- DBScan
DBScan
Density-based Spatial Clustering of Applications With Noise Points are:
- Core - within \( \epsilon \) of \( p \) (min points).
- Reachable - within \( \epsilon \) of a core point.
- Outliner - neither are true.
DBScan
Look at iris again
library("dbscan")
data(iris)
iris <- as.matrix(iris[,1:4])
res <- dbscan(iris, eps = .5, minPts = 5)
res
DBSCAN clustering for 150 objects.
Parameters: eps = 0.5, minPts = 5
The clustering contains 2 cluster(s) and 17 noise points.
0 1 2
17 49 84
Available fields: cluster, eps, minPts
DBScan
Look at iris again
library("dbscan")
kNNdistplot(USArrests, k = 5)
eps = 20
abline(h=eps, col = "red", lty=2)
res <- dbscan(USArrests, eps = eps, minPts = 3)
res
DBSCAN clustering for 50 objects.
Parameters: eps = 20, minPts = 3
The clustering contains 5 cluster(s) and 10 noise points.
0 1 2 3 4 5
10 7 3 10 9 11
Available fields: cluster, eps, minPts
DBScan
arrests = USArrests
arrests$cluster = factor(res$cluster)
arrests[arrests$cluster ==1,]
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape cluster
Alabama 13.2 236 58 21.2 1
Delaware 5.9 238 72 15.8 1
Illinois 10.4 249 83 24.0 1
Louisiana 15.4 249 66 22.2 1
Michigan 12.1 255 74 35.1 1
Nevada 12.2 252 81 46.0 1
New York 11.1 254 86 26.1 1
arrests[arrests$cluster ==2,]
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape cluster
Arizona 8.1 294 80 31.0 2
Maryland 11.3 300 67 27.8 2
New Mexico 11.4 285 70 32.1 2
arrests[arrests$cluster ==3,]
Murder Assault UrbanPop Rape cluster
Connecticut 3.3 110 77 11.1 3
Idaho 2.6 120 54 14.2 3
Indiana 7.2 113 65 21.0 3
Kansas 6.0 115 66 18.0 3
Kentucky 9.7 109 52 16.3 3
Montana 6.0 109 53 16.4 3
Nebraska 4.3 102 62 16.5 3
Ohio 7.3 120 75 21.4 3
Pennsylvania 6.3 106 72 14.9 3
Utah 3.2 120 80 22.9 3
DBScan
arrests = USArrests
arrests$cluster = factor(res$cluster)
ggpairs(arrests, mapping=ggplot2::aes(fill=cluster,color=cluster))
DBScan
Scale fields with differing mean/variance in order to prevent one dimension from dominating the NN cluster metric
res <- dbscan(scale(USArrests), eps = 1, minPts = 3)
res
DBSCAN clustering for 50 objects.
Parameters: eps = 1, minPts = 3
The clustering contains 4 cluster(s) and 9 noise points.
0 1 2 3 4
9 6 29 3 3
Available fields: cluster, eps, minPts
DBScan
arrests = USArrests
arrests$cluster = factor(res$cluster)
ggpairs(arrests, mapping=ggplot2::aes(fill=cluster,color=cluster))
DBScan
Strengths:
- Does not require cluster count parameter
- Finds arbitrary shapes with consistent density
- Avoid “thin line” effect of hierarchical clustering
- Excludes outliers from clusters (i.e. can eliminate noise)
- Requires two parameters
- (Mostly) invariant to ordering
Weaknesses:
- Non-deterministic clusters possible during “ties” among neighbors
- Suffers from curse of dimensionality issues
- Doesn't handle clusters of differing density
- Relies on expert knowledge to set \( \epsilon \) and \( p \).
- Expensive algorithm \( O(n^2) \), although pre-indexing can yield \( O(log(n)) \).
DBScan
See Also : OPTICS
- “Ordering Points to Identify The Clustering Structure”
- Overcomes density variance between clusters problem in DBScan
Graph-based Clustering
- HCS
HCS
Highly Connected Subgraph
- Find the minimum cut on a graph
- Partition graph into two subgraphs
- Recursively run on the subgraphs
HCS
# source("https://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R")
# biocLite("RBGL")
# biocLite("Rgraphviz")
library(RBGL)
library(Rgraphviz)
con <- file(system.file("XML/conn.gxl",package="RBGL"), open="r")
coex <- fromGXL(con)
coex
A graphNEL graph with undirected edges
Number of Nodes = 8
Number of Edges = 14
HCS
plot(coex)
HCS
plot(coex)
highlyConnSG(coex)
$clusters
$clusters[[1]]
[1] "A" "B" "C" "D"
$clusters[[2]]
[1] "E" "H" "F" "G"
MCL
MCL - Markov Cluster Algorithm
- Process has four phases:
- (Optional-required for directed graphs) add self links
- “Expansion” through standard matrix multiplication
- “Inflation” through column wise exponentiation (I) and renormalization
- Rinse and repeat
Picture courtesy of http://micans.org and Stijn van Dongen
MCL
MCL works with adjacency matrices
library(MCL)
adjacency <- matrix(c(0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,1,1,
0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,
0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0),
byrow=TRUE, nrow=9)
library(igraph)
gu<-graph.adjacency(adjacency, mode="undirected")
plot(gu)
MCL
Here we're running mcl and adding optional self-loops, and returning an equlibrium state matrix.
res = mcl(x = adjacency, addLoops=TRUE, ESM = TRUE)
res
$K
[1] 3
$n.iterations
[1] 14
$Cluster
[1] 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 0 0
$Equilibrium.state.matrix
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
6 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
MCL
We can use igraph to plot the network with our clusters
plot(graph.adjacency(adjacency), vertex.color = res$Cluster)
Clustering Technique Recap
- In general, learn as much as possible about the data before trying to cluster.
- Do you know the expected number of clusters?
- Do you know anything about the distribution?
- Do you know if the data is graph-like?
- Simplify structure when/where appropriate (sparsification, network pruningu
- Consider combining clustering with dimensionality reduction (coming soon!)
Clustering Deep Dive
imdb top 5000 movies
imdb
dat = read.csv("movie_metadata.csv")
str(dat)
'data.frame': 5043 obs. of 28 variables:
$ color : chr "Color" "Color" "Color" "Color" ...
$ director_name : chr "James Cameron" "Gore Verbinski" "Sam Mendes" "Christopher Nolan" ...
$ num_critic_for_reviews : int 723 302 602 813 NA 462 392 324 635 375 ...
$ duration : int 178 169 148 164 NA 132 156 100 141 153 ...
$ director_facebook_likes : int 0 563 0 22000 131 475 0 15 0 282 ...
$ actor_3_facebook_likes : int 855 1000 161 23000 NA 530 4000 284 19000 10000 ...
$ actor_2_name : chr "Joel David Moore" "Orlando Bloom" "Rory Kinnear" "Christian Bale" ...
$ actor_1_facebook_likes : int 1000 40000 11000 27000 131 640 24000 799 26000 25000 ...
$ gross : int 760505847 309404152 200074175 448130642 NA 73058679 336530303 200807262 458991599 301956980 ...
$ genres : chr "Action|Adventure|Fantasy|Sci-Fi" "Action|Adventure|Fantasy" "Action|Adventure|Thriller" "Action|Thriller" ...
$ actor_1_name : chr "CCH Pounder" "Johnny Depp" "Christoph Waltz" "Tom Hardy" ...
$ movie_title : chr "Avatar " "Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End " "Spectre " "The Dark Knight Rises " ...
$ num_voted_users : int 886204 471220 275868 1144337 8 212204 383056 294810 462669 321795 ...
$ cast_total_facebook_likes: int 4834 48350 11700 106759 143 1873 46055 2036 92000 58753 ...
$ actor_3_name : chr "Wes Studi" "Jack Davenport" "Stephanie Sigman" "Joseph Gordon-Levitt" ...
$ facenumber_in_poster : int 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 4 3 ...
$ plot_keywords : chr "avatar|future|marine|native|paraplegic" "goddess|marriage ceremony|marriage proposal|pirate|singapore" "bomb|espionage|sequel|spy|terrorist" "deception|imprisonment|lawlessness|police officer|terrorist plot" ...
$ movie_imdb_link : chr "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0499549/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1" "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0449088/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1" "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt2379713/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1" "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt1345836/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1" ...
$ num_user_for_reviews : int 3054 1238 994 2701 NA 738 1902 387 1117 973 ...
$ language : chr "English" "English" "English" "English" ...
$ country : chr "USA" "USA" "UK" "USA" ...
$ content_rating : chr "PG-13" "PG-13" "PG-13" "PG-13" ...
$ budget : num 2.37e+08 3.00e+08 2.45e+08 2.50e+08 NA ...
$ title_year : int 2009 2007 2015 2012 NA 2012 2007 2010 2015 2009 ...
$ actor_2_facebook_likes : int 936 5000 393 23000 12 632 11000 553 21000 11000 ...
$ imdb_score : num 7.9 7.1 6.8 8.5 7.1 6.6 6.2 7.8 7.5 7.5 ...
$ aspect_ratio : num 1.78 2.35 2.35 2.35 NA 2.35 2.35 1.85 2.35 2.35 ...
$ movie_facebook_likes : int 33000 0 85000 164000 0 24000 0 29000 118000 10000 ...
imdb
sapply(dat, is.numeric)
color director_name
FALSE FALSE
num_critic_for_reviews duration
TRUE TRUE
director_facebook_likes actor_3_facebook_likes
TRUE TRUE
actor_2_name actor_1_facebook_likes
FALSE TRUE
gross genres
TRUE FALSE
actor_1_name movie_title
FALSE FALSE
num_voted_users cast_total_facebook_likes
TRUE TRUE
actor_3_name facenumber_in_poster
FALSE TRUE
plot_keywords movie_imdb_link
FALSE FALSE
num_user_for_reviews language
TRUE FALSE
country content_rating
FALSE FALSE
budget title_year
TRUE TRUE
actor_2_facebook_likes imdb_score
TRUE TRUE
aspect_ratio movie_facebook_likes
TRUE TRUE
imdb
dat_nums = dat[,sapply(dat, is.numeric)]
str(dat_nums)
'data.frame': 5043 obs. of 16 variables:
$ num_critic_for_reviews : int 723 302 602 813 NA 462 392 324 635 375 ...
$ duration : int 178 169 148 164 NA 132 156 100 141 153 ...
$ director_facebook_likes : int 0 563 0 22000 131 475 0 15 0 282 ...
$ actor_3_facebook_likes : int 855 1000 161 23000 NA 530 4000 284 19000 10000 ...
$ actor_1_facebook_likes : int 1000 40000 11000 27000 131 640 24000 799 26000 25000 ...
$ gross : int 760505847 309404152 200074175 448130642 NA 73058679 336530303 200807262 458991599 301956980 ...
$ num_voted_users : int 886204 471220 275868 1144337 8 212204 383056 294810 462669 321795 ...
$ cast_total_facebook_likes: int 4834 48350 11700 106759 143 1873 46055 2036 92000 58753 ...
$ facenumber_in_poster : int 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 4 3 ...
$ num_user_for_reviews : int 3054 1238 994 2701 NA 738 1902 387 1117 973 ...
$ budget : num 2.37e+08 3.00e+08 2.45e+08 2.50e+08 NA ...
$ title_year : int 2009 2007 2015 2012 NA 2012 2007 2010 2015 2009 ...
$ actor_2_facebook_likes : int 936 5000 393 23000 12 632 11000 553 21000 11000 ...
$ imdb_score : num 7.9 7.1 6.8 8.5 7.1 6.6 6.2 7.8 7.5 7.5 ...
$ aspect_ratio : num 1.78 2.35 2.35 2.35 NA 2.35 2.35 1.85 2.35 2.35 ...
$ movie_facebook_likes : int 33000 0 85000 164000 0 24000 0 29000 118000 10000 ...
imdb
mdat = melt(dat_nums, id.vars=c("imdb_score"))
ggplot(mdat, aes(fill=factor(as.integer(imdb_score)), x=value)) +
geom_histogram() +
facet_wrap(~variable, scales="free")
imdb
It can help to scale
mdat = melt(dat_nums, id.vars=c("imdb_score"))
ggplot(mdat, aes(fill=factor(as.integer(imdb_score)), x=value)) +
geom_histogram() +
scale_x_log10() +
facet_wrap(~variable, scales="free")
imdb
mdat = melt(dat_nums, id.vars=c("imdb_score"))
ggplot(mdat, aes(factor(as.integer(imdb_score)), value)) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape=NA) +
facet_wrap(~variable, scales="free_y")
imdb
It can help to scale
mdat = melt(dat_nums, id.vars=c("imdb_score"))
ggplot(mdat, aes(factor(as.integer(imdb_score)), value)) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape=NA) +
scale_y_log10() +
facet_wrap(~variable, scales="free_y")
imdb
Impute the means
dat_num_imp = sapply(dat_nums, function(x) {x[is.na(x)]<-mean(x,na.rm=T); x})
any(is.na(dat_num_imp))
[1] FALSE
imdb
Using raw data produces very uneven clusters:
kdat = kmeans(dat_num_imp, 3)
dat$cluster = kdat$cluster
ggplot(dat, aes(x=cluster,fill=factor(cluster))) + geom_histogram(stat="count")
imdb
Scaling issues in fields (budget) are dominating cluster categories:
t = table(dat$cluster)
t
1 2 3
1 4678 364
small = names(t)[which.min(t)]
dat[dat$cluster == as.integer(small),c("movie_title", "language", "budget", "cluster")]
movie_title language budget cluster
2989 The Host Korean 12215500000 1
median(dat$budget,na.rm=T)
[1] 2e+07
imdb
We can scale the data so it has the same column-wise mean/variance:
dat_scaled = as.data.frame(scale(dat_num_imp))
kdat = kmeans(dat_scaled, 3)
table(kdat$cluster)
1 2 3
4164 765 114
ds = dat_scaled
ds$cluster = kdat$cluster
dat$cluster = kdat$cluster
mdat = melt(ds, id.vars=c("cluster"))
imdb
ggplot(mdat, aes(fill=factor(cluster), x=value)) +
geom_histogram() + scale_x_log10() +
facet_wrap(~variable, scales="free")
imdb
ggplot(mdat, aes(factor(cluster), value)) +
geom_boxplot(outlier.shape=NA) + scale_y_log10() +
facet_wrap(~variable, scales="free_y")
imdb
library(FNN)
closest = function(k){
ds = dat_scaled[kdat$cluster ==k,]
idx = get.knnx(ds, query = t(kdat$center[k,]))$nn.index[1]
idx
str(dat[kdat$cluster==k,][idx,])
}
imdb
closest(1)
'data.frame': 1 obs. of 29 variables:
$ color : chr "Color"
$ director_name : chr "Andrzej Bartkowiak"
$ num_critic_for_reviews : int 109
$ duration : int 101
$ director_facebook_likes : int 43
$ actor_3_facebook_likes : int 432
$ actor_2_name : chr "Tom Arnold"
$ actor_1_facebook_likes : int 5000
$ gross : int 34604054
$ genres : chr "Action|Crime|Drama|Thriller"
$ actor_1_name : chr "Jet Li"
$ movie_title : chr "Cradle 2 the Grave "
$ num_voted_users : int 34942
$ cast_total_facebook_likes: int 6867
$ actor_3_name : chr "DMX"
$ facenumber_in_poster : int 2
$ plot_keywords : chr "camera shot from inside human body|diamond|evil man|heist|terrorism"
$ movie_imdb_link : chr "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0306685/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1"
$ num_user_for_reviews : int 185
$ language : chr "English"
$ country : chr "USA"
$ content_rating : chr "R"
$ budget : num 3e+07
$ title_year : int 2003
$ actor_2_facebook_likes : int 618
$ imdb_score : num 5.8
$ aspect_ratio : num 2.35
$ movie_facebook_likes : int 1000
$ cluster : int 1
imdb
closest(2)
'data.frame': 1 obs. of 29 variables:
$ color : chr "Color"
$ director_name : chr "Gabriele Muccino"
$ num_critic_for_reviews : int 202
$ duration : int 123
$ director_facebook_likes : int 125
$ actor_3_facebook_likes : int 835
$ actor_2_name : chr "Rosario Dawson"
$ actor_1_facebook_likes : int 10000
$ gross : int 69951824
$ genres : chr "Drama|Romance"
$ actor_1_name : chr "Will Smith"
$ movie_title : chr "Seven Pounds "
$ num_voted_users : int 232710
$ cast_total_facebook_likes: int 14727
$ actor_3_name : chr "Madison Pettis"
$ facenumber_in_poster : int 1
$ plot_keywords : chr "boyfriend girlfriend relationship|heart|main character dies|organ donor|redemption"
$ movie_imdb_link : chr "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0814314/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1"
$ num_user_for_reviews : int 599
$ language : chr "English"
$ country : chr "USA"
$ content_rating : chr "PG-13"
$ budget : num 5.5e+07
$ title_year : int 2008
$ actor_2_facebook_likes : int 3000
$ imdb_score : num 7.7
$ aspect_ratio : num 2.35
$ movie_facebook_likes : int 26000
$ cluster : int 2
imdb
closest(3)
'data.frame': 1 obs. of 29 variables:
$ color : chr "Color"
$ director_name : chr "Rupert Sanders"
$ num_critic_for_reviews : int 416
$ duration : int 132
$ director_facebook_likes : int 274
$ actor_3_facebook_likes : int 11000
$ actor_2_name : chr "Kristen Stewart"
$ actor_1_facebook_likes : int 26000
$ gross : int 155111815
$ genres : chr "Action|Adventure|Drama|Fantasy"
$ actor_1_name : chr "Chris Hemsworth"
$ movie_title : chr "Snow White and the Huntsman "
$ num_voted_users : int 228554
$ cast_total_facebook_likes: int 72881
$ actor_3_name : chr "Sam Claflin"
$ facenumber_in_poster : int 0
$ plot_keywords : chr "evil queen|fairy tale|magic|queen|snow white"
$ movie_imdb_link : chr "http://www.imdb.com/title/tt1735898/?ref_=fn_tt_tt_1"
$ num_user_for_reviews : int 710
$ language : chr "English"
$ country : chr "USA"
$ content_rating : chr "PG-13"
$ budget : num 1.7e+08
$ title_year : int 2012
$ actor_2_facebook_likes : int 17000
$ imdb_score : num 6.1
$ aspect_ratio : num 2.35
$ movie_facebook_likes : int 53000
$ cluster : int 3
imdb
Possible cluster labels?
- Critically Acclaimed (higher imdb score and number of raters)
- Popular with the Masses (higher fb likes, crowd pleaser)
- Mediocre/mixed popularity